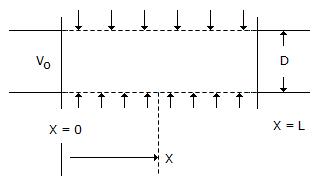
A pipe has a porous section of length L as shown in the figure. Velocity at the start of this section of V0. If fluid leaks into the pipe through the porous section at a volumetric rate per unit area q(x/L)2, what will be axial velocity in the pipe at any x ? Assume incompressible one dimensional flow i.e., no gradients in the radial direction.
 |