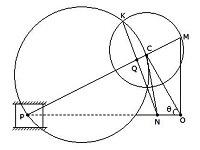
In the below figure, PC is the connecting rod and OC is the crank making an angle θ with the line of stroke PO and rotates with uniform angular velocity at ω rad/s. The Klien's acceleration diagram for determining the acceleration of the piston P is shown by quadrilateral CQNO, if N coincides with O, then